AI-Driven Autonomous Vehicles: Challenges and Opportunities on US Roads

AI-driven autonomous vehicles (AVs) promise to revolutionize US roads, offering increased safety, efficiency, and accessibility while also presenting complex challenges like regulatory hurdles, ethical considerations, and technological limitations.
The advent of AI-driven autonomous vehicles: navigating the challenges and opportunities on US roads, marks a pivotal moment in transportation history. These self-driving cars, powered by sophisticated artificial intelligence, hold the potential to reshape our cities, highways, and daily lives.
Understanding AI-Driven Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles (AVs), also known as self-driving cars, utilize a combination of sensors, cameras, radar, and artificial intelligence (AI) to navigate and operate without human input. These vehicles aim to enhance safety, reduce traffic congestion, and improve accessibility for individuals who cannot drive.
Levels of Automation in AVs
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has defined six levels of driving automation, ranging from 0 (no automation) to 5 (full automation). Understanding these levels is crucial in assessing the current state and future trajectory of autonomous vehicle technology.
- Level 0: No Automation – The human driver controls all aspects of the vehicle.
- Level 1: Driver Assistance – The vehicle offers limited assistance, such as adaptive cruise control or lane keeping.
- Level 2: Partial Automation – The vehicle can control steering and acceleration/deceleration under certain conditions, but the driver must remain attentive and ready to intervene.
- Level 3: Conditional Automation – The vehicle can perform all driving tasks under specific conditions, such as highway driving, but the driver must be ready to take control when prompted.
- Level 4: High Automation – The vehicle can perform all driving tasks under specific conditions without human intervention, but it may not be able to handle all scenarios.
- Level 5: Full Automation – The vehicle can perform all driving tasks under all conditions without human intervention.
Key Technologies Behind Autonomous Vehicles
Several core technologies enable autonomous vehicles to function effectively. These include:
- Computer Vision: Using cameras and AI algorithms to interpret visual data, such as traffic signals, pedestrians, and lane markings.
- Sensor Fusion: Combining data from various sensors (e.g., radar, LiDAR) to create a comprehensive understanding of the vehicle’s surroundings.
- Path Planning: Utilizing AI to determine the optimal route and make real-time decisions to avoid obstacles and navigate roadways.
- Machine Learning: Training AI models to recognize patterns, predict behavior, and improve decision-making over time.
In conclusion, understanding the levels of automation and the underlying technologies is essential for grasping the potential and complexities of AI-driven autonomous vehicles. These advancements are paving the way for a future where transportation is safer, more efficient, and more accessible.
The Potential Benefits of Autonomous Vehicles
The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles holds the promise of numerous benefits, ranging from improved safety and reduced congestion to increased accessibility for underserved populations. Let’s delve into some of the most significant advantages.
Enhanced Safety on the Roads
One of the primary drivers behind the development of autonomous vehicles is the potential to significantly reduce traffic accidents. Human error is a major contributor to accidents, and AVs, with their advanced sensors and AI-driven decision-making, can mitigate many of these errors.
Reduced Traffic Congestion and Improved Efficiency
Autonomous vehicles have the potential to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve overall transportation efficiency. By coordinating movements and maintaining consistent speeds, AVs can minimize stop-and-go traffic.
- Platooning: AVs can travel in close proximity to each other, reducing drag and improving fuel efficiency.
- Optimized Routing: AI algorithms can analyze real-time traffic data to determine the most efficient routes for vehicles.
- Reduced Parking Needs: With the rise of ride-sharing services, AVs could decrease the demand for parking spaces in urban areas.
Increased Accessibility for Underserved Populations
Autonomous vehicles can greatly enhance mobility for individuals who are unable to drive, such as the elderly, people with disabilities, and those living in areas with limited transportation options. AVs can provide on-demand transportation, empowering these individuals to access employment, healthcare, and social opportunities.
In summary, the potential benefits of autonomous vehicles are vast and far-reaching. From enhancing safety and reducing congestion to improving accessibility and promoting sustainability, AVs have the power to transform the way we move and interact with our environment.
Challenges and Obstacles Facing AV Deployment
While the potential benefits of autonomous vehicles are compelling, numerous challenges and obstacles remain before large-scale deployment can be realized. These challenges span technical, regulatory, ethical, and social domains.
Technical Hurdles and Limitations
Despite significant advancements in AI and sensor technology, autonomous vehicles still face technical limitations in certain conditions. Inclement weather, such as heavy rain, snow, or fog, can impair the performance of sensors and algorithms, leading to safety concerns.
Regulatory and Legal Frameworks
The current regulatory and legal frameworks surrounding autonomous vehicles are still evolving. Governments and regulatory bodies are grappling with questions of liability, safety standards, and data privacy.
Ethical Considerations and Moral Dilemmas
Autonomous vehicles raise complex ethical considerations, particularly in scenarios involving unavoidable accidents. Programmers must decide how the vehicle should prioritize the safety of its occupants versus other road users.
Overcoming these challenges requires collaboration among stakeholders, including automakers, technology companies, regulators, and the public. By addressing these hurdles proactively and transparently, we can pave the way for the safe and responsible deployment of autonomous vehicles.
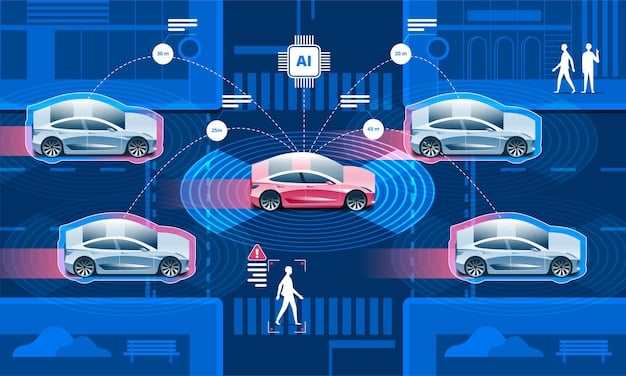
The Role of Government and Regulation
Government at the state and federal levels will play a crucial role in shaping the future of autonomous vehicles. Creating clear, consistent, and adaptable regulatory frameworks is essential for ensuring safety, promoting innovation, and building public trust.
Federal Oversight and Standards
At the federal level, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has the authority to set safety standards for motor vehicles, including autonomous vehicles.
State-Level Regulations and Pilot Programs
Many states have already enacted legislation or executive orders to govern the testing and deployment of autonomous vehicles. These regulations vary widely, reflecting different priorities and approaches.
- California: A leader in autonomous vehicle testing, California requires companies to obtain permits for testing AVs on public roads.
- Arizona: Known for its welcoming regulatory environment, Arizona has attracted numerous companies to test and deploy AVs.
- Texas: Texas has established a framework for autonomous vehicle operations, focusing on safety and innovation.
Public Engagement and Education
Effective regulation also requires public engagement and education. Policymakers must address public concerns about safety, privacy, and job displacement. Efforts must also be made to educate the public about the benefits and limitations of AV technology.
In conclusion, the role of government and regulation is vital in steering the development and deployment of autonomous vehicles. By establishing clear standards, fostering innovation, and engaging with the public, policymakers can help unlock the full potential of AV technology while mitigating risks.
The Economic and Societal Impact of AVs
The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles is poised to have a profound impact on the economy and society. While some of these effects are expected to be positive, others raise concerns that must be addressed proactively.
Job Displacement and Workforce Transition
One of the most significant concerns surrounding autonomous vehicles is the potential for job displacement, particularly among professional drivers. Truck drivers, taxi drivers, and delivery drivers could see their jobs threatened as AV technology advances.
Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development
Autonomous vehicles have the potential to reshape urban landscapes and infrastructure needs. With the rise of ride-sharing services, cities may need fewer parking spaces.
Accessibility and Social Equity
Autonomous vehicles can greatly enhance accessibility for individuals who are unable to drive, such as the elderly, people with disabilities, and those living in areas with limited transportation options.
Overall, the economic and societal impacts of autonomous vehicles are complex and multi-faceted. While AVs offer the potential to improve efficiency, safety, and accessibility, careful planning and proactive policies are needed to mitigate potential negative consequences, such as job displacement and social inequity.
Future Trends and Predictions for Autonomous Vehicles
The field of autonomous vehicles is rapidly evolving, with ongoing research, development, and innovation driving progress. Looking ahead, several key trends and predictions offer insights into the future of AV technology.
Advancements in AI and Machine Learning
Continued advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will be critical for improving the performance and reliability of autonomous vehicles. AI algorithms will become more sophisticated, enabling AVs to better understand their surroundings.
- Deep Learning: Deep learning techniques will enable AVs to recognize complex patterns and make more accurate predictions.
- Reinforcement Learning: Reinforcement learning algorithms will allow AVs to learn from experience and adapt to new situations.
Integration with Smart City Infrastructure
Autonomous vehicles will increasingly integrate with smart city infrastructure, enabling seamless communication and coordination. Smart traffic management systems will use real-time data from AVs to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🚗 Safety Enhancement | AVs reduce accidents by minimizing human error with advanced sensors and AI. |
| 🚦 Traffic Efficiency | AVs optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion through coordinated movements. |
| 🧑🤝🧑 Accessibility | AVs improve mobility for non-drivers, enhancing their access to opportunities. |
| ⚖️ Regulatory Impact | Government regulations are crucial for ensuring safe and responsible AV deployment. |
FAQ
Autonomous Vehicles?
▼
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) are vehicles capable of sensing their environment and operating without human input. They use sensors, cameras, and AI to navigate roads, interpret traffic signals, and avoid obstacles.
What are the main benefits of AI-driven autonomous vehicles?
▼
The main benefits include enhanced safety by reducing human error, improved traffic efficiency by optimizing traffic flow, increased accessibility for non-drivers, and potential environmental benefits through optimized fuel consumption.
What are the primary challenges facing the deployment of AVs?
▼
Challenges include technical limitations such as performance in adverse weather, regulatory uncertainties around liability and safety standards, ethical considerations in accident scenarios, and public acceptance of self-driving technology.
How will autonomous vehicles impact urban planning and infrastructure?
▼
AVs can reshape urban areas by reducing parking needs, optimizing traffic patterns, and enabling more efficient public transportation. Infrastructure may need to adapt to support AV communication and charging needs.
What is the role of government in regulating autonomous vehicles?
▼
Government plays a critical role in setting safety standards, defining liability frameworks, ensuring data privacy, and managing the social and economic impacts of AVs through regulations and public policies.





